
The 555 timer IC is an integrated circuit (chip) used in a variety of timer, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. The 555 can be used to provide time delays, as an oscillator, and as a flip-flop element. Derivatives provide up to four timing circuits in one package.
 The NE555 parts were commercial temperature range, 0 °C to +70 °C, and the SE555
part number designated the military temperature range, −55 °C to +125
°C. These were available in both high-reliability metal can (T package)
and inexpensive epoxy plastic (V package) packages. Thus the full part
numbers were NE555V, NE555T, SE555V, and SE555T. It has been
hypothesized that the 555 got its name from the three 5 kΩ resistors used within, but Hans Camenzind has stated that the number was arbitrary.
The NE555 parts were commercial temperature range, 0 °C to +70 °C, and the SE555
part number designated the military temperature range, −55 °C to +125
°C. These were available in both high-reliability metal can (T package)
and inexpensive epoxy plastic (V package) packages. Thus the full part
numbers were NE555V, NE555T, SE555V, and SE555T. It has been
hypothesized that the 555 got its name from the three 5 kΩ resistors used within, but Hans Camenzind has stated that the number was arbitrary. Low-power versions of the 555 are also available, such as the 7555 and CMOS TLC555. The 7555 is designed to cause less supply noise than the classic 555
and the manufacturer claims that it usually does not require a "control"
capacitor and in many cases does not require a decoupling capacitor
on the power supply. Those parts should generally be included, however,
because noise produced by the timer or variation in power supply
voltage might interfere with other parts of a circuit or influence its
threshold voltages.
Low-power versions of the 555 are also available, such as the 7555 and CMOS TLC555. The 7555 is designed to cause less supply noise than the classic 555
and the manufacturer claims that it usually does not require a "control"
capacitor and in many cases does not require a decoupling capacitor
on the power supply. Those parts should generally be included, however,
because noise produced by the timer or variation in power supply
voltage might interfere with other parts of a circuit or influence its
threshold voltages.Modes
The IC 555 has three operating modes:- Bistable mode or Schmitt trigger – the 555 can operate as a flip-flop, if the DIS pin is not connected and no capacitor is used. Uses include bounce-free latched switches.
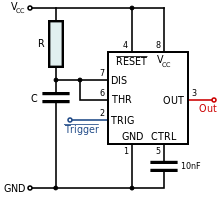
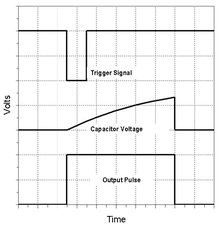
- Monostable mode – in this mode, the 555 functions as a "one-shot" pulse generator. Applications include timers, missing pulse detection, bounce-free switches, touch switches, frequency divider, capacitance measurement, pulse-width modulation (PWM) and so on.
- Astable (free-running) mode – the 555 can operate as an electronic oscillator. Uses include LED and lamp flashers, pulse generation, logic clocks, tone generation, security alarms, pulse position modulation and so on. The 555 can be used as a simple ADC, converting an analog value to a pulse length (e.g., selecting a thermistor as timing resistor allows the use of the 555 in a temperature sensor and the period of the output pulse is determined by the temperature). The use of a microprocessor-based circuit can then convert the pulse period to temperature, linearize it and even provide calibration means.
Bistable
Schematic of a 555 in bistable mode
Monostable
See also: RC circuit
Schematic of a 555 in monostable mode
The output pulse width of time t, which is the time it takes to charge C to 2/3 of the supply voltage, is given by
Pins
Pinout diagram
| Pin | Name | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground reference voltage, low level (0 V) |
| 2 | TRIG | The OUT pin goes high and a timing interval starts when this input falls below 1/2 of CTRL voltage (which is typically 1/3 VCC, CTRL being 2/3 VCC by default if CTRL is left open). More simply we can say that OUT will be high as long as the trigger is kept at low voltage. Output of the timer totally depends upon the amplitude of the external trigger voltage applied to this pin. |
| 3 | OUT | This output is driven to approximately 1.7 V below +VCC, or to GND. |
| 4 | RESET | A timing interval may be reset by driving this input to GND, but the timing does not begin again until RESET rises above approximately 0.7 volts. Overrides TRIG which overrides THR. |
| 5 | CTRL | Provides "control" access to the internal voltage divider (by default, 2/3 VCC). |
| 6 | THR | The timing (OUT high) interval ends when the voltage at THR ("threshold") is greater than that at CTRL (2/3 VCC if CTRL is open). |
| 7 | DIS | Open collector output which may discharge a capacitor between intervals. In phase with output. |
| 8 | VCC | Positive supply voltage, which is usually between 3 and 15 V depending on the variation. |

No comments:
Post a Comment